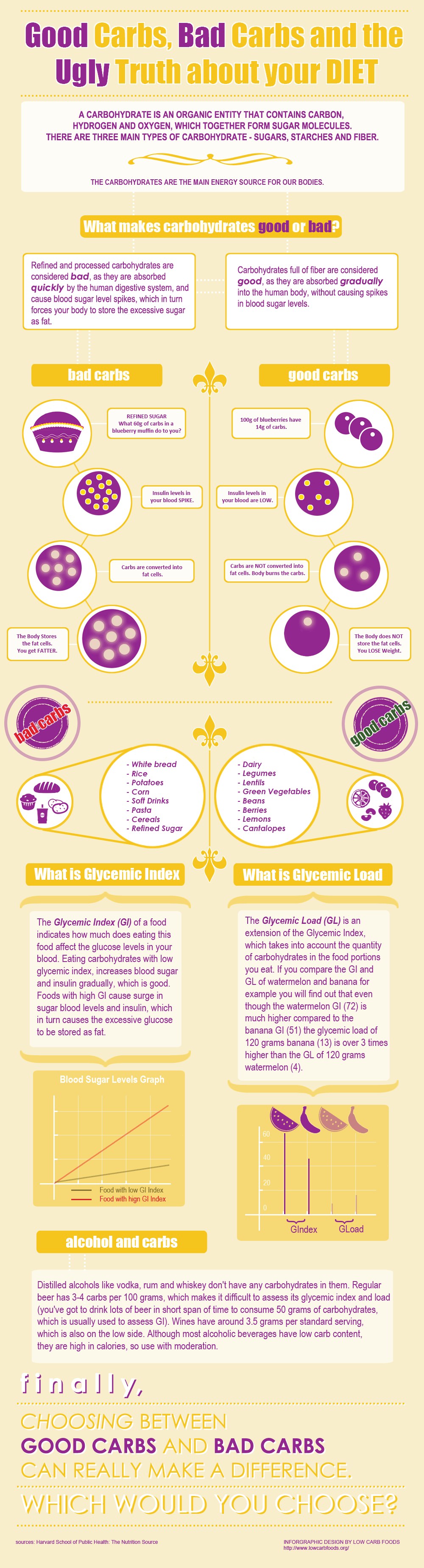
Good Carbs vs. Bad Carbs
This info graph is about the benefits of low carbohydrate foods and explains the difference between "good" carbs and "bad" carbs. Learn why you gain weight when eating "bad"carbs and why you lose weight when eating "good" carbs. Learn about Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load and the choices you can make for a better lifestyle. Feel free to use the infographic below on your website, as long as you link to the original page where it was first published: Embedding the infographic on your blog or website is very easy and you'll find instructions how to do it here. The infographic is licensed through the Creative Commons Attribution-No Derivatives License which allows redistribution both commercial and noncommercial as long as it is unchanged and credited to Low Carb Foods.org.
Embed this Infographic on your site using the HTML code below:
Good carbs vs. Bad Carbs infographic offers information about carbohydrates, grouping foods into two broad categories - those with good carbs and bad carbs. The main difference between them is in the way they are processed. Bad carbs are simple carbohydrates, which the body absorbs faster, and this leads to a rapid increase in blood sugar levels.
The infographic further illustrates how good and bad carbohydrates affect insulin levels, with carbs being stored as fat cells or burnt. It gives examples of foods (e.g. pasta and rice) that contain bad carbs and such that supply good carbs, such as berries and beans. The grouping into foods that contain bad and good carbohydrates helps dieters choose products that are suitable for a healthy low-carb diet. Some foods, especially those with added sugars, have no or few nutrients. Thus, they supply calories and are of little nutritional value. Moreover, foods that contain bad carbs are often loaded with preservatives, flavorings, colorings, and other additives. Additives improve desirable qualities but are associated with sudden cardiac death, inflammations, obesity, the development of tumors, and other medical problems and complications.
Unlike them, good carbohydrates are nutritious, and foods that contain them are rich in fiber, minerals, and vitamins. They are also rich in substances that aid toxin removal and help dieters maintain normal cholesterol levels. This is especially important for people who suffer from diabetes because they have to monitor their blood glucose.
One can find information about the glycemic index and glycemic load, as well as the effect of foods with low and high glycemic values on insulin and blood sugar levels. Learn about the impact of foods with high and low GI index on blood sugar and the difference between glycemic index and load by comparing two fruits (watermelon and banana).
Dieters learn how to compare the GL and GI of different foods. This is important so that they can choose carbohydrates with a low glycemic index and load. The lower the GI level of a food is, the better for the human body. Such foods raise blood sugar levels at a slower rate and lower the risk for diabetes, obesity, and heart disease. According to researchers at the Harvard University, a healthy diet consists of vegetables, beans, and whole grains, which contain good carbs.
Finally, it informs dieters about carbohydrates in alcohol, with examples of distilled alcohols that contain no carbs. Other types of alcohols have small amounts of carbohydrates, making it difficult to assess their GL and GI. The problem with alcohol is its calorie content, which is why it is important to drink in moderation.
Good carbohydrates are an essential component of a healthy low-carb diet. While bad carb foods are tasty, they are associated with blood sugar related conditions such as insulin resistance, diabetes, hypoglycemia, and others. A balanced diet should include mostly complex or good carbohydrates, as well as healthy proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and fiber.

